Advice on MIM design
1.Integration

2.Avoiding parts with a thick wall
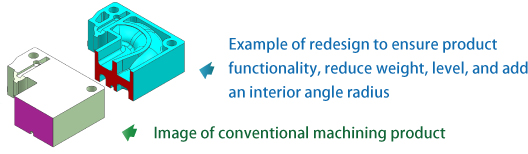
Because a part with a thick wall is likely to have a molding defect and/or a debinding fault, it is leveled (approximately 1.5 to 2.5 mm) by thinning, ribbing, or other means.
3.Leveling and weight reduction
4.Corner radius
When contracting with low strength, a tensile force is easily generated at the interior angle radius. A small radius is added to disperse the force.
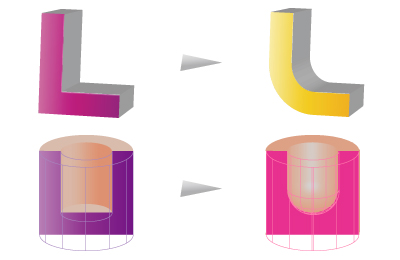
5.Example of weight reduction
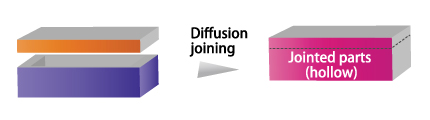
Composite
| Joining the same materials | Achieving thick products for which MIM is difficult (For MIM, it is normally difficult to manufacture a product with a thickness of 5 mm or more in terms of molding and debinding.) |
|---|---|
Achieving undercut products for which metal tooling cannot be molded integrally (example: hollow parts, etc.) |
Example of joining

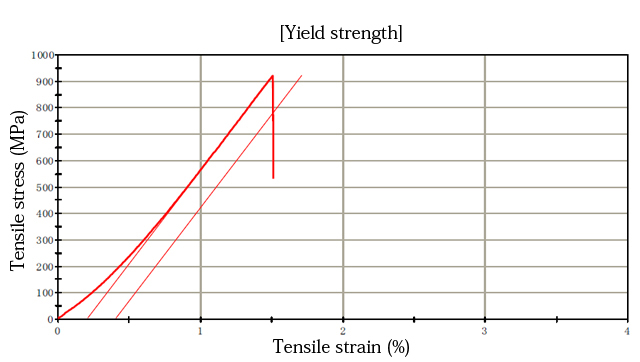
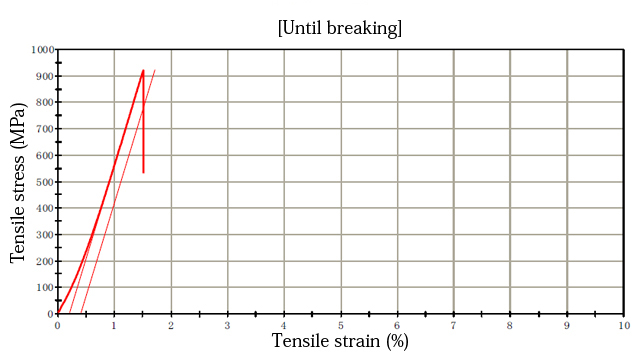
Evaluation of material properties
Representative mechanical properties are described in the material list. However, we can perform property evaluations specified by customers
Diameter: 2.524 mm Gauge length: 20.00 mm Test temperature: 23ºC
| Maximum load(kN) | Tensile strength(MPa) | Elongation | Drawing | Break position | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.619 |
923 |
-100.0 |
100.0 |
C |
Tensile speed: 0.5 mm/min
| Measurement item | Unit | Measured temperature °C | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | ||
| Thermal conductivity | W/cm・K |
0.1242 |
0.1445 |
0.1619 |
0.1790 |
0.1993 |
0.2214 |
0.2469 |
0.2791 |
0.2909 |
| Specific heat | J/g・K |
0.3971 |
0.4367 |
0.4538 |
0.4672 |
0.4855 |
0.5086 |
0.5366 |
0.5761 |
0.5858 |
| Linear expansion coefficient | 10-6/K |
- |
10.93 |
11.59 |
12.07 |
12.49 |
12.91 |
13.40 |
13.87 |
14.20 |
| Young's modulus | GPa |
271.3 |
268.0 |
262.0 |
254.9 |
247.8 |
239.5 |
229.1 |
217.8 |
200.1 |
| Poisson's ratio | - |
0.30 |
0.30 |
0.30 |
0.30 |
0.30 |
0.30 |
0.29 |
0.28 |
0.25 |
| Density | g/c㎥ |
8.862 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
*The above date are shown only for reference, and are not necessarily guaranteed for actual Proterial Precision products.